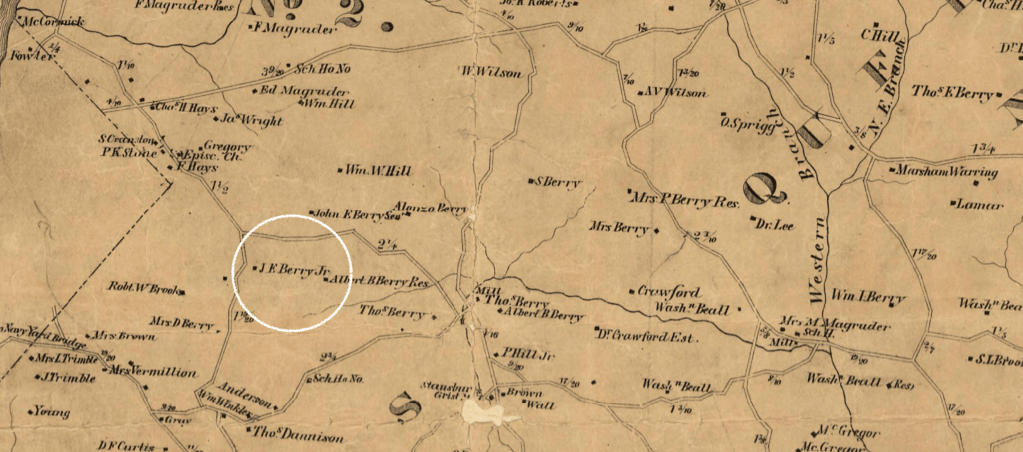
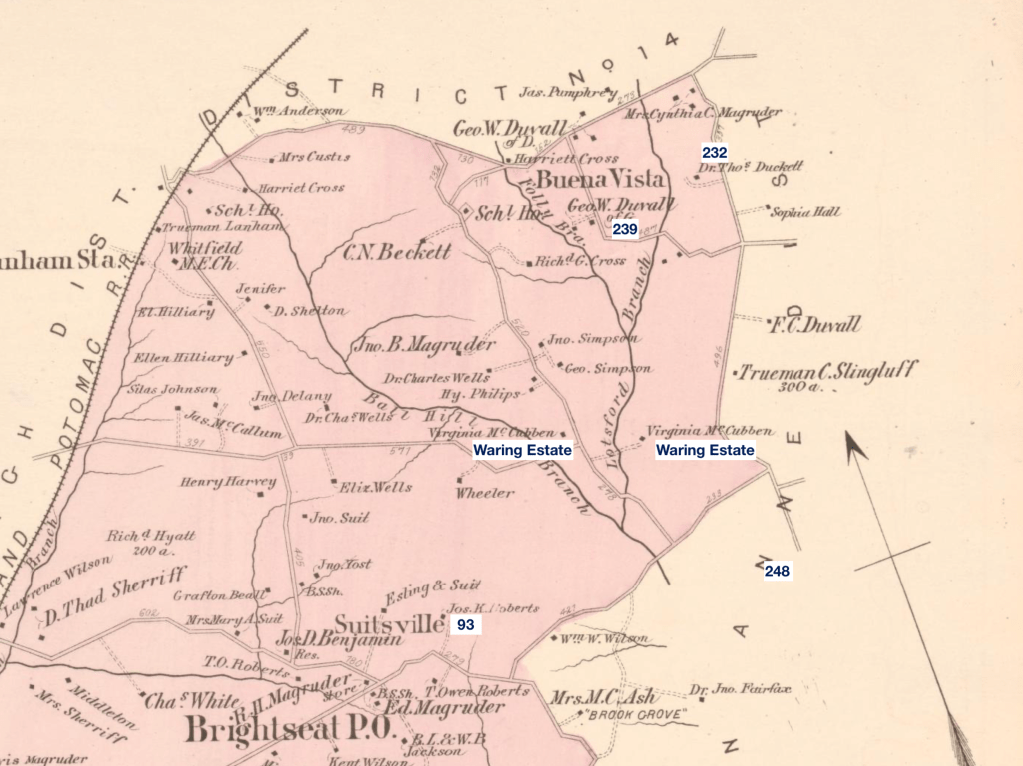
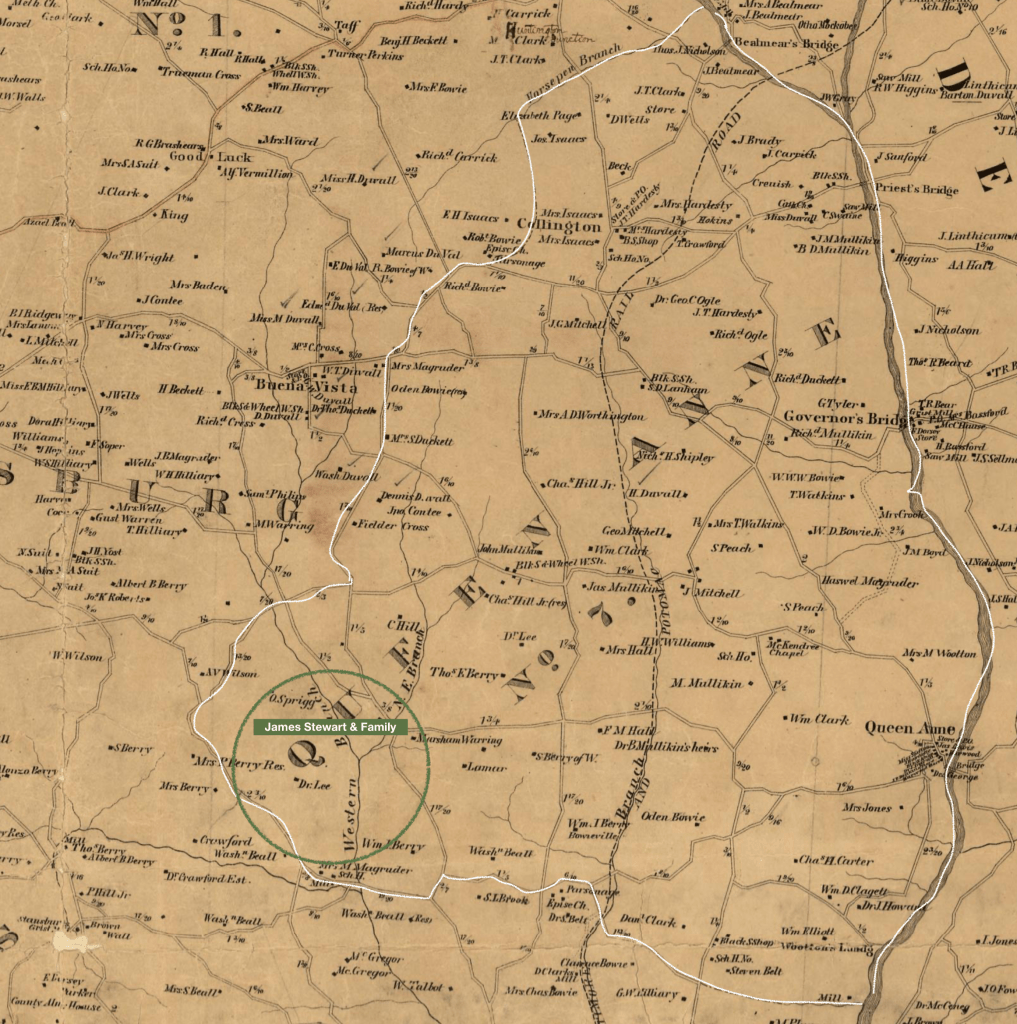
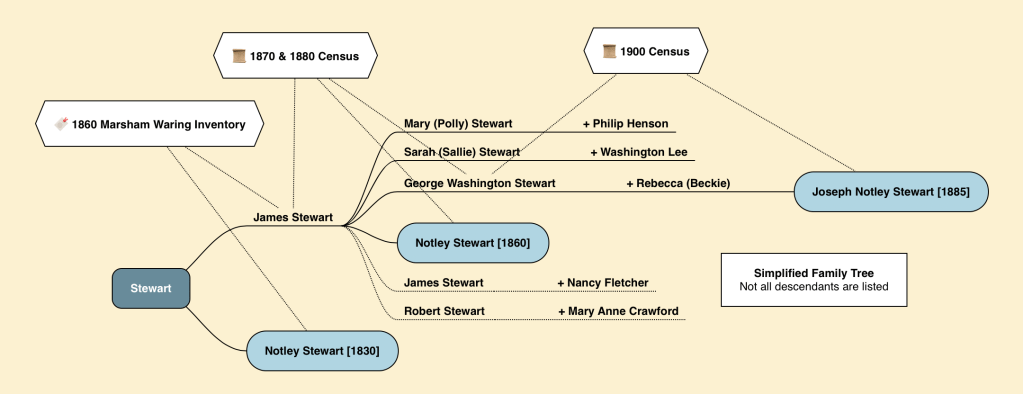
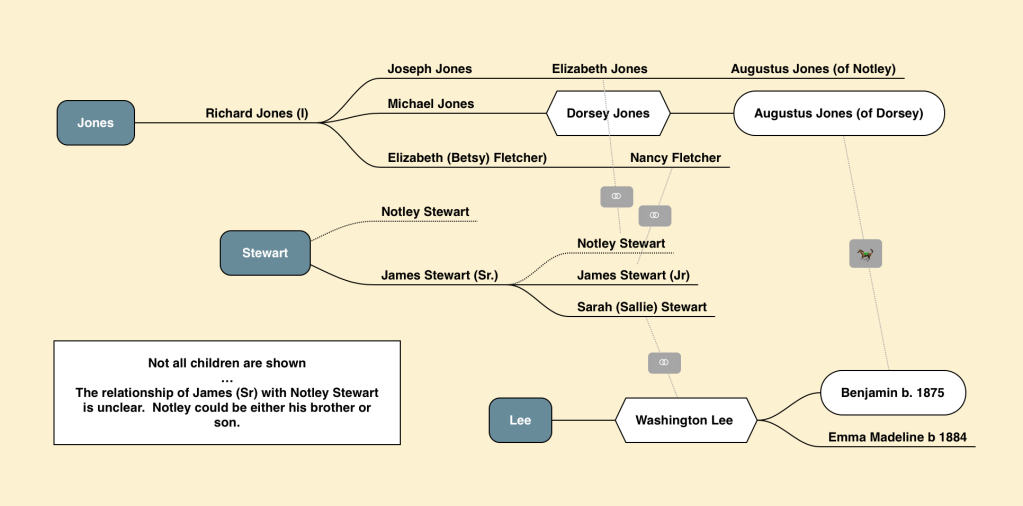
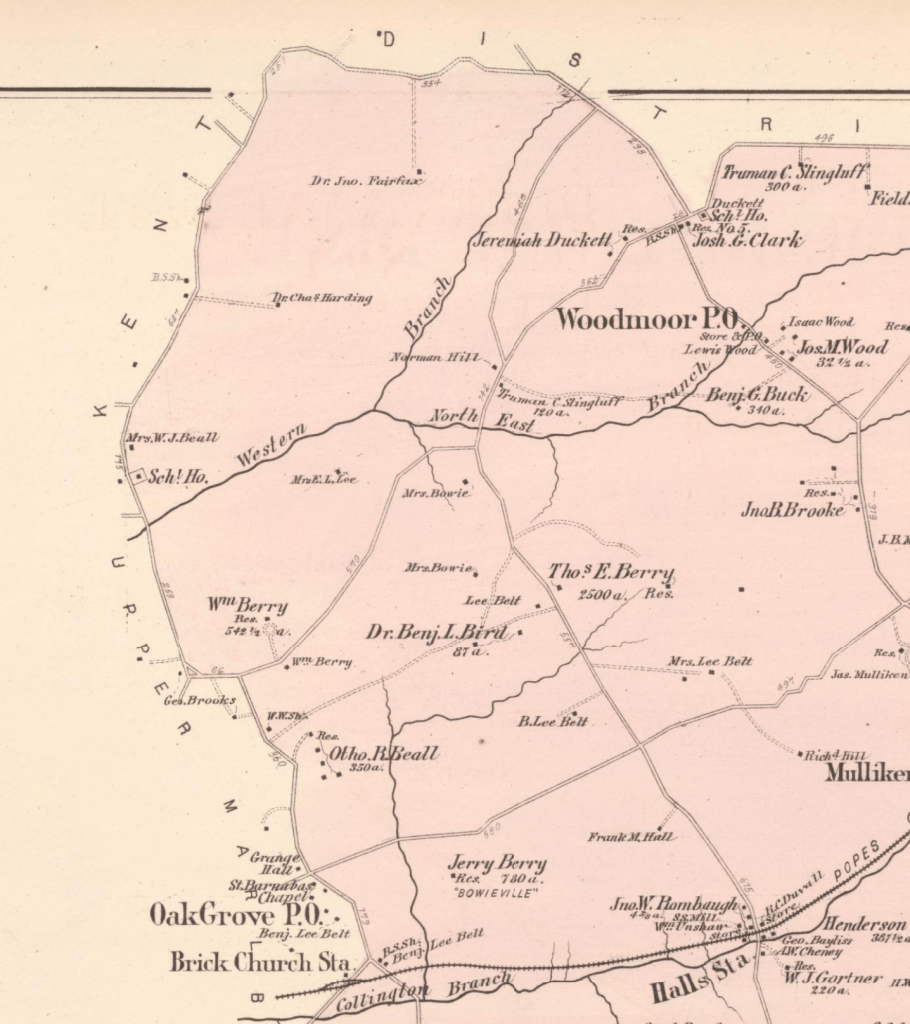
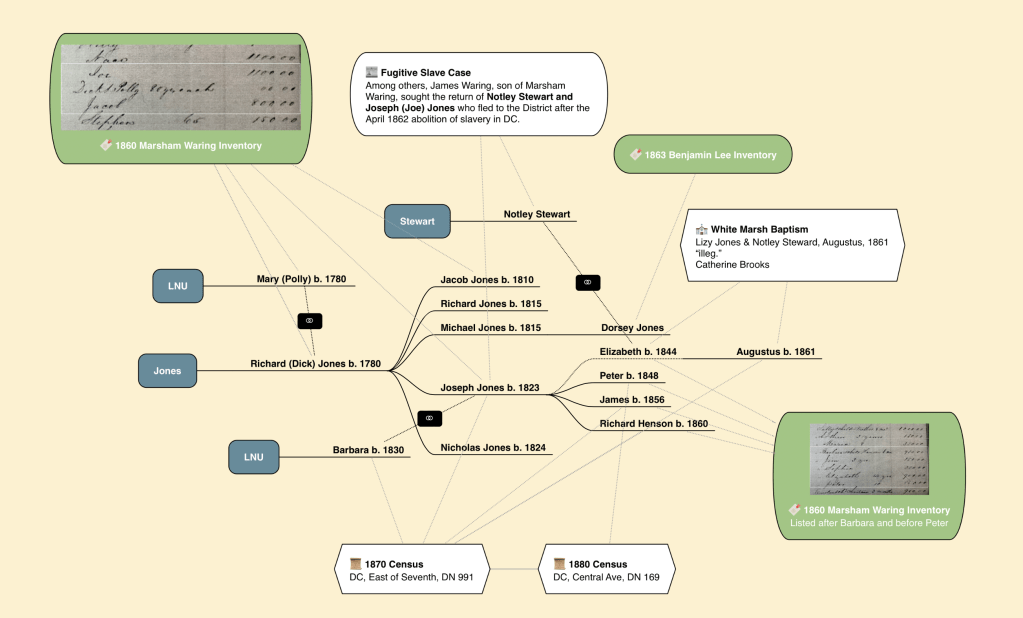
James Stewart (Jr) and his wife, Ann (Nancy) Fletcher, liberated themselves during the Civil War from their enslavement in Prince George’s County. Nancy was enslaved by Marsham Waring and his heirs, while her husband was enslaved by Waring’s brother-in-law, Benjamin Lee. Both Waring and Lee were large landowners along the Western Branch in Queen Anne District.
Following the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia in 1862, neighboring enslaved individuals seized an opportunity for freedom. Despite monitored roads and patrols, many fled their bondage and headed toward the District. Barbara Jeanne Fields highlighted in her book, Slavery and Freedom on the Middle Ground that “Many an ex-fugitive later reported having left Maryland for the District during or after the spring of 1862. Families packed up such of their possessions as could be compactly assembled and departed, sometimes appropriating means of transportation from their owners.” (111)
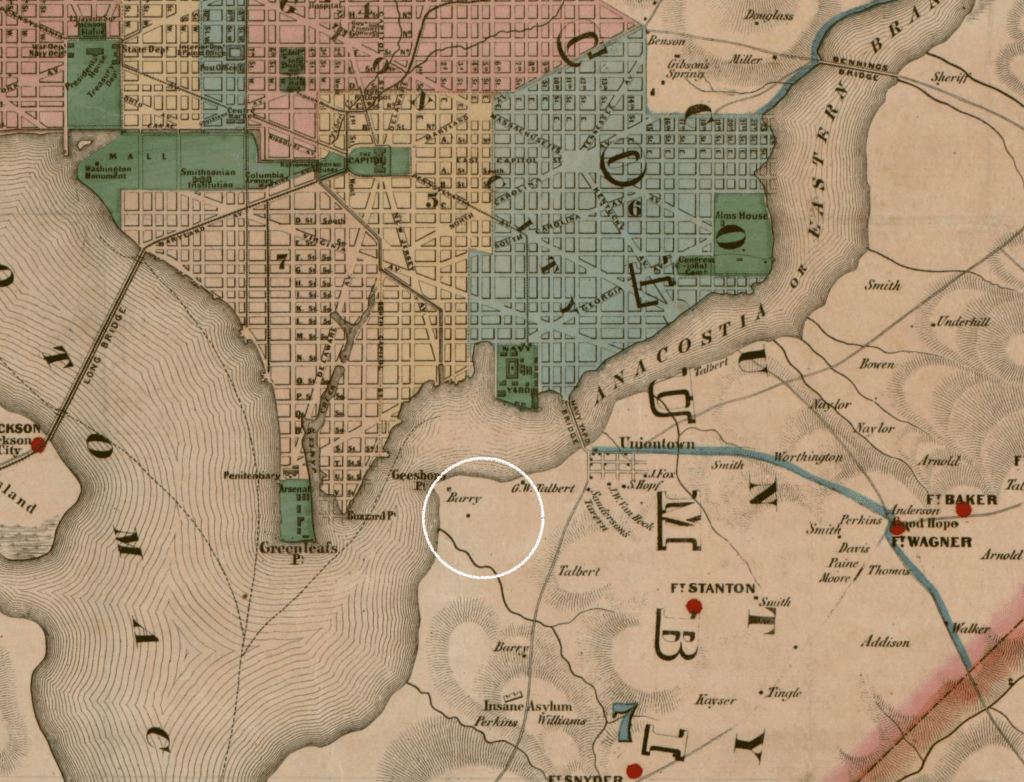
Camps emerged in and around the District to accommodate these incoming refugees from slavery. One such camp, Camp Springdale, comprised of tents on the grounds of the “Arlington Estate,” owned by Robert E. Lee’s wife. James and Nancy Stewart were recorded as residents of Camp Springdale in 1864 along with their three children: John (Henson), George (Anthony), and Frances. During this time, Nancy was a new mother, taking care of her infant daughter and her older sons.

Post-War Life
1870
James and Nancy survived the war with their sons. After the war, they are living in the District, as recorded by the 1870 Census. Living in Ward 5, James is working as a scavenger while Nancy is “keeping house”. Scavenger is a euphemism, like night-soil man, for a person who collected human waste from households and transported the waste away from residential areas. The Evening Star reported in 1869, that because there was no designated place for depositing the “night soil”, it was dumped into the Potomac, the Tiber creek and the Canal.
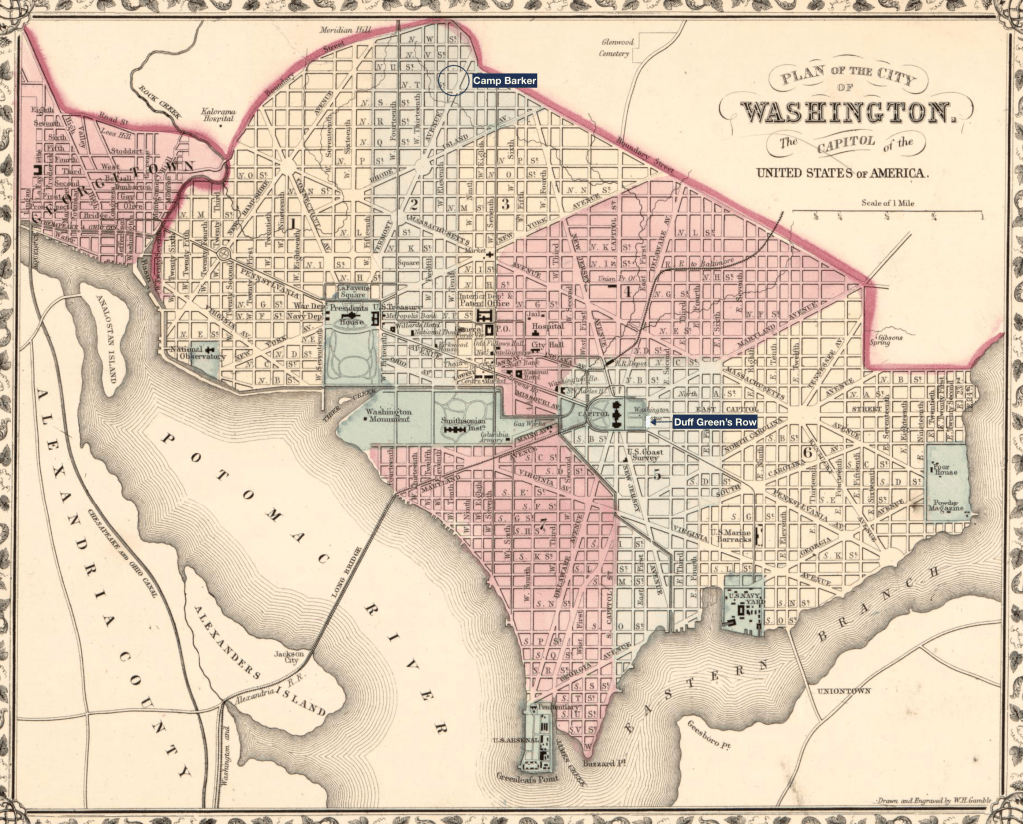
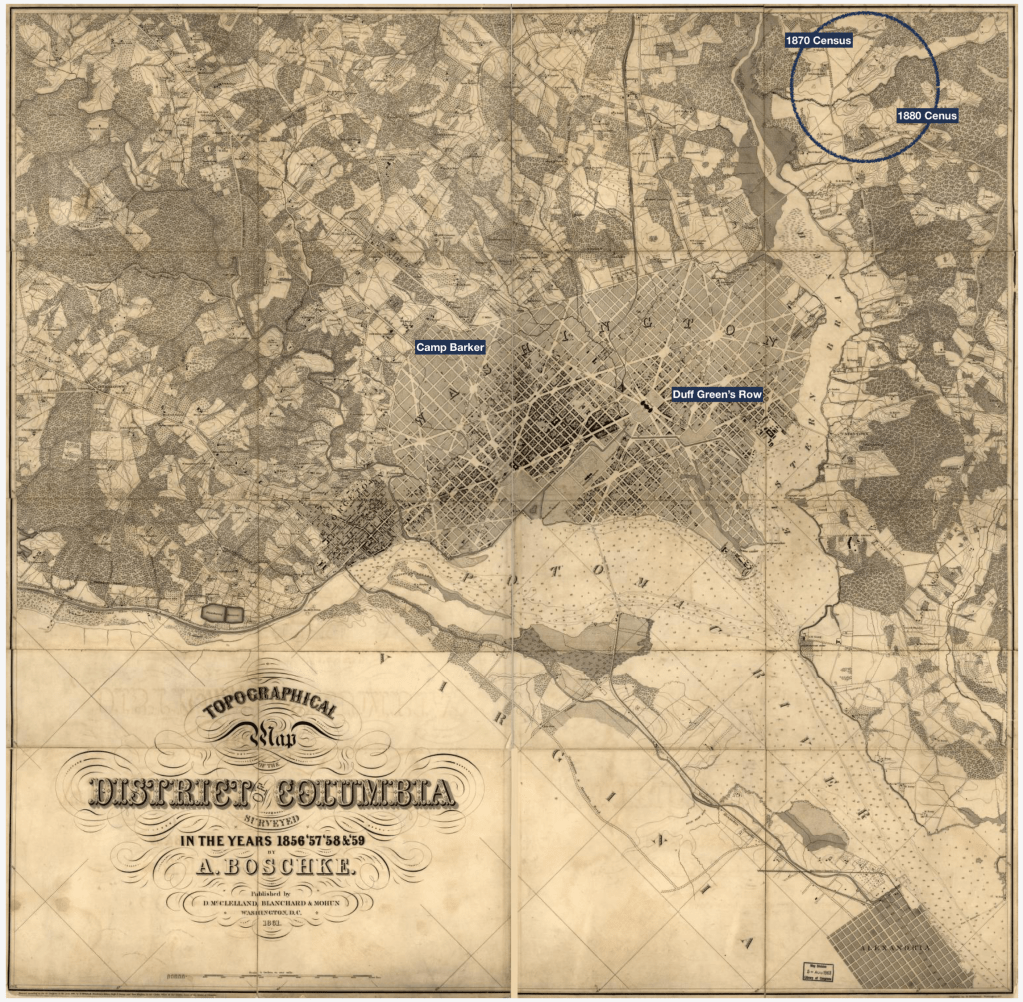
The 1870 Census did not record addresses or street names (like in later census records), however, by comparing names in the Census to the City Directories, a more precise location can be determined. The Stewart Family is enumerated immediately after Benton Russ, a guard at the Jail; in the City Directory, Benton Russ is recorded as living at 2d and A NE, near the location of another refugee camp, Duff’s Green Row.
1880
By 1880, the family appears to have been split up by economic necessity. Three separate census records have been identified that appear to represent the family based on the geographic proximity to their 1870 address of 2d and A NE. Nancy is living at 107 2nd NE while Ella and John Henson are working as servants at nearby addresses. George Anthony has yet to be found.
Nancy Stewart is enumerated in her household, a widow. Ella, age 12, is working as a servant at 18 2nd Street NE in the household of Isaac Bassett, a doorman at the Capitol Building. Both addresses are clustered around the intersection of A St NE and 2nd St NE.
(John) Henson Stewart is working in the household of Mary J Wheeler, who lived at 136 Pennsylvania Ave SE, which was at the the intersection of Independence Ave SE (then B St SE) and 2nd St SE. Essentially, Nancy and Ella lived by the Supreme Court and John Henson Stewart lived by the Library of Congress, a few short blocks away with East Capitol Street separating them.
On the other hand, George (Anthony) is much more elusive. George Stewart was a common name and several men with the name were working as servants in city; none were near George Anthony’s family members. In 1885, a city directory entry records Anthony Steward living as a laborer at Bassett Alley NE, which is one block north of where Nancy Stewart was living in 1880.
1900
By 1900, Nancy Stewart has moved east of Lincoln Park and is living at 15 Fitzhugh Court, SE with her two sons: John and George A. She is living with Mary Jones, who is listed as her sister in the census record.
Although the census lists inaccurate ages for them, shaving decades off of their ages, the address aligns with other records that suggest the high probability that this is the same family. The following records support this connection:
- 1907 City Directory entry for Nancy Stewart, wid. James, residing at 15 Fitzugh Court SE
- 1910 Census Entry for Nancy Stewart and John at 15 Fitzhugh Court, the age of Nancy is 71, aligning more closely with previous records.
- 1919 Death Record for a widowed Nancy Stewart living at 15 Fitzhugh Court, with burial in Mt. Olivet, a Catholic Cemetery