Lewis and Beck Medley, enslaved by Carroll family in St. Mary’s County escaped slavery by leaving with the British during the War of 1812. In the post [Lewis and Beck Medley | the British came], I speculated that because the Carroll family were neighbors to the Sewall family and both the Carrolls and the Sewall enslaved family groups with the names Lewis & Beck, that Lewis & Beck Medley may have been related to the Beck family group listed in the 1822 Robert Sewall Inventory of St. Mary’s County Property [TT 5:25].
| 1814 Claim | 1822 Inventory |
|---|---|
| Lewis Medley, 21 [1793] | Beck, 45 [1777] |
| Beck Medley, 17 [1797] | Lewis, 16 [1806] |
| | Milley, 13 [1809] |
| | Barney, 11 [1811] |
| | Sam, 7 [1815] |
Compensation for “Manumission”
Further documentation has been found to provide more information about the relationship between the two families.
In 1865, the Dangerfield Heirs of Robert D Sewall’s estate filed multiple Deeds of Manumission in Prince George’s County Land Records [FS 3:33-41 | mdlandrec.net]. These manumissions were filed in August 1865, almost a full year after the passage of the November 1864 Maryland Constitution which emancipated all enslaved people in Maryland. The manumissions effectively did not change the status of the named individuals as they had been previously freed by the State of Maryland.
Instead, these manumissions were filed in hopes of compensation for slaves who had been used by the US Army. In 1863, the US Government began to compensate slaveholders for the enlistment of enslaved people if they could prove their status. By filing the deed of manumission, the enslavers hoped to prove ownership of the enslaved people and receive $300 “upon filing a “manumission” or deed of ownership”. [US National Archives]. Multiple enslavers named those they had enslaved who enlisted in the FS Libers of the Prince George’s County Land Records. Some enslavers named the date of enlistment and the regiment within which the enslaved mustered. In the eleven manumissions filed by the Dangerfield Heirs, none stated a date of enlistment or regiment.
Basil Medley was one of the enslaved people named in the manumissions by the Dangerfield Heirs. USCT records have been located for him under the name “Bazil Medley” (fold3.com | ancestry.com)
Basil Medley was described as a 5 foot 6 inches man, 21 years old. He had brown skin with black eyes and hair. His birth (likely 1843) was listed as Prince George’s County, about ten years after Robert D Sewall inherited the St. Mary’s property and three years after Robert D Sewall sold the St. Mary’s property to George Forbes in 1840, consolidating his holdings in Prince George’s County.
Basil Medley enlisted into Company H of the 23rd Regiment in Washington DC in the spring of 1864. He signed his enlistment papers with his mark.

1853 Inventory
In the 1853 Robert D Sewall Inventory [JH 2:699], there is a family group that included the names Lewis and Basil.
It is in the portion of the inventory that lists the people “gifted” to William P Brinham and on the property in his possession. Brinham was a friend of both Robert D Sewall and Sewall’s brother, William HB. William HB Sewall had inherited the St. Mary’s property from his father in 1820 and upon his death in 1832 had devised it to Robert D Sewall. In the 1840s, Sewall had conveyed some of those who had previously been enslaved in St Mary’s county to Brinham [JBB 3:587]. Listed in the deed are “Louis and his wife Maria, and their children, to wit: Mary and John Louis.”
These names correspond with the first two children listed in the Lewis family group in the 1853 inventory.
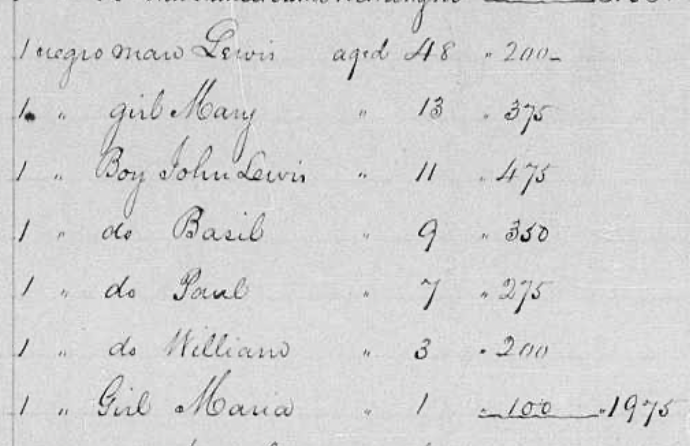
In the family group, Lewis is listed as the inferred father, at 48 years old. This places his estimated birth year as 1805, which is consistent with the 1822 St. Mary’s inventory which estimates his birth year as 1806. The two inventories alone however did not indicate a surname name for either family. This left it open as to whether or not Beck and her children were related to the Lewis Medley who escaped the Carrolls and his Medleys, or related to his wife, Beck, and therefore related to a different family surname.
The USCT records cite Basil’s last name as Medley, which suggests that Lewis (born 1805/6) was also a Medley.

The presence of Medley for Basil suggests that Beck’s children and grandchildren are related to Lewis Medley who left with the British in 1812. It is likely that Beck’s partner and Lewis’s father is the Medley.
